My Dog Has Pale Gums, What Should I Do? Our Vet Explains

Updated on

The color of your dog’s gums can tell you a great deal about their health. A healthy dog should have pink and moist gums; they shouldn’t feel tacky or be another color. If your dog’s gums have a different color (yellow, pale white, blue, purple, or red), it means they may have a health problem, and it’s time to contact the veterinarian.
In this article, find out what it means when a dog has pale gums and what you should do about it, along with what a dog’s gums normally look like.
Normal Gums vs. Pale Gums in Dogs
Healthy dogs should have moist and pink gums, close to the color of cooked salmon. If you press your finger on a pink area, it should turn white and then return to pink in about a second.
If your dog has pigmented mucous membranes, it may be more difficult to tell how pink their gums are. In this situation, look for light spots on the gums, under the tongue, or your dog’s eyes (gently pull the eyelid down and look at the color of the tissue).
When the gums are pale or have a color other than pink, it can be a sign of one or more underlying conditions. In addition, when a dog has pale gums, they will also have pale ocular mucosa. If this is also the case with your dog, you should contact your vet immediately.
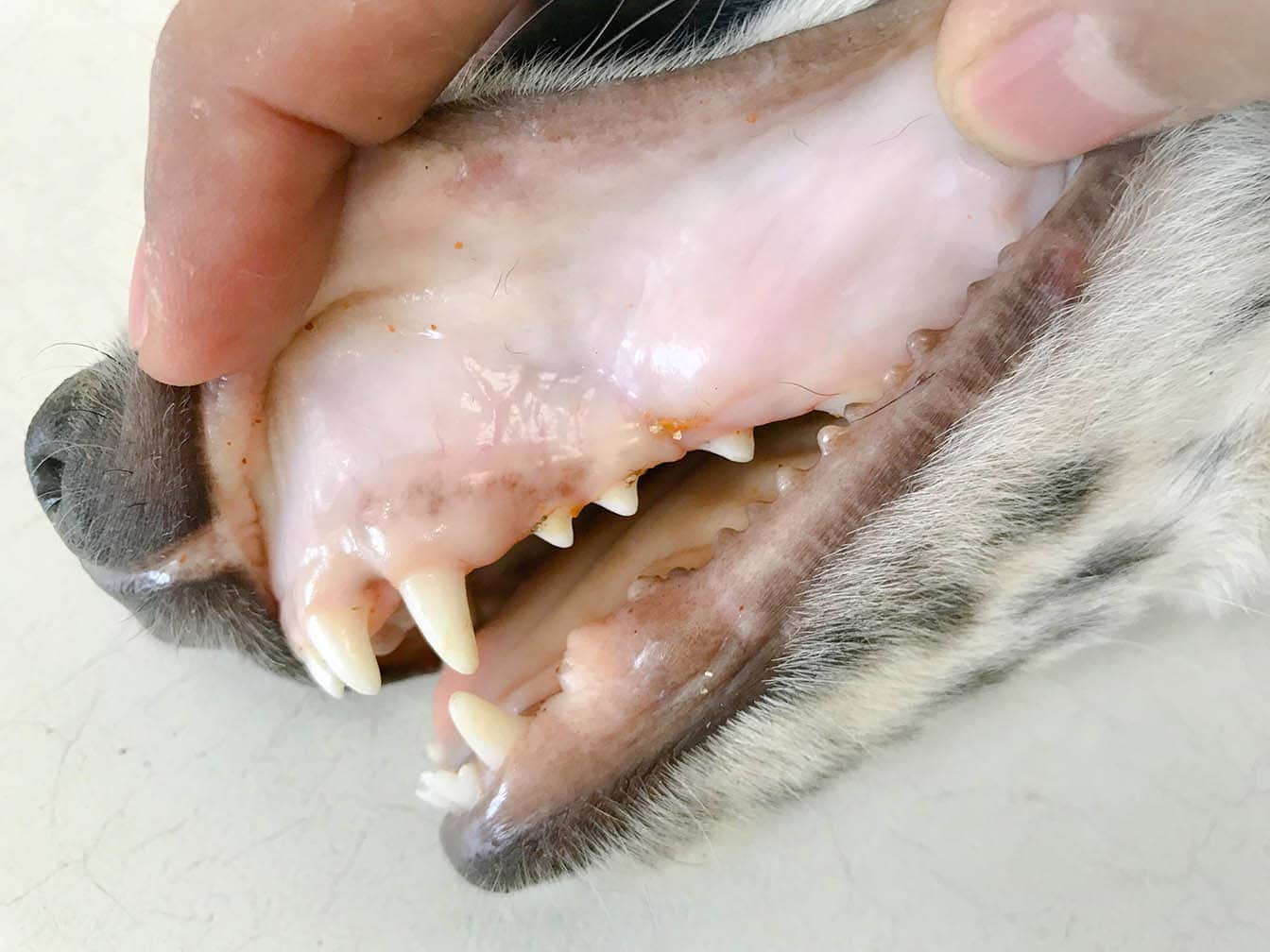
Reasons Why Dog’s Gums Are Pale
Healthy dogs do not have pale gums, and several health problems can have this as a clinical sign. The most common ones that can lead to pale gums in dogs are as follows.
1. Diseases That Cause Anemia
Pale gums can indicate that dogs are suffering from anemia, which can be caused by several conditions, such as internal bleeding, kidney disease, hemolysis, low production of red cells, immune-mediated disorders, parasitosis, intoxication/poisoning, shock, etc.
Anemia is not a disease, as it’s just what occurs when there are not enough red cells in the blood. When this happens, the body’s cells can’t get enough oxygen, and they may die.
2. Blood Loss
When there is internal bleeding, not enough blood can circulate in the body, which leads to anemia. The blood flow to mucous membranes, including the gums, decreases, making them look pale.
Massive blood loss (whether external or internal) can have multiple causes, such as tumors, internal injuries, trauma, ulcers, fractures, etc. You can observe the following clinical signs:
- Pale gums
- Fatigue/weakness
- Lethargy
- Dark-colored stools and vomiting with blood (when the bleeding occurs in the digestive tract)
- Bruises on the skin
- Collapse
If your dog shows these clinical signs, contact the veterinarian as soon as possible.
3. Hemolysis
Hemolysis, i.e., the destruction of red cells, causes anemia and thus implicitly, pale gums. It can occur as a result of various conditions, such as autoimmune hemolytic anemia, intracellular parasites (Babesia canis), cancer, etc. Hemolysis can also occur when a dog is exposed to toxic substances like onions, garlic, leeks, or rat poison. The clinical signs will be specific to each individual condition.

4. Decreased Production of Red Blood Cells
Certain kidney or liver diseases, autoimmune diseases, hypothyroidism, nutritional imbalances, exposure to chemicals/toxins, or cancer can lead to a decrease in the production of red blood cells. As in the case of hemolysis, the clinical signs will be specific to each condition.
5. Blood-Clotting Disorders
In the case of blood-clotting disorders, the blood does not clot normally, and the affected dog is prone to abnormal and excessive bleeding. These disorders occur in conditions like thrombocytopenia and thrombocytopathies (platelet disorders), kidney diseases, cancer, etc. Clinical signs may include:
- Pale gums (anemia)
- Prolonged bleeding (for example, a small scratch that bleeds excessively)
- Blood in the urine or stool
- Bruising and petechiae on the skin
- Nose bleeds
Take your dog to the vet if they show these clinical signs.
6. Shock
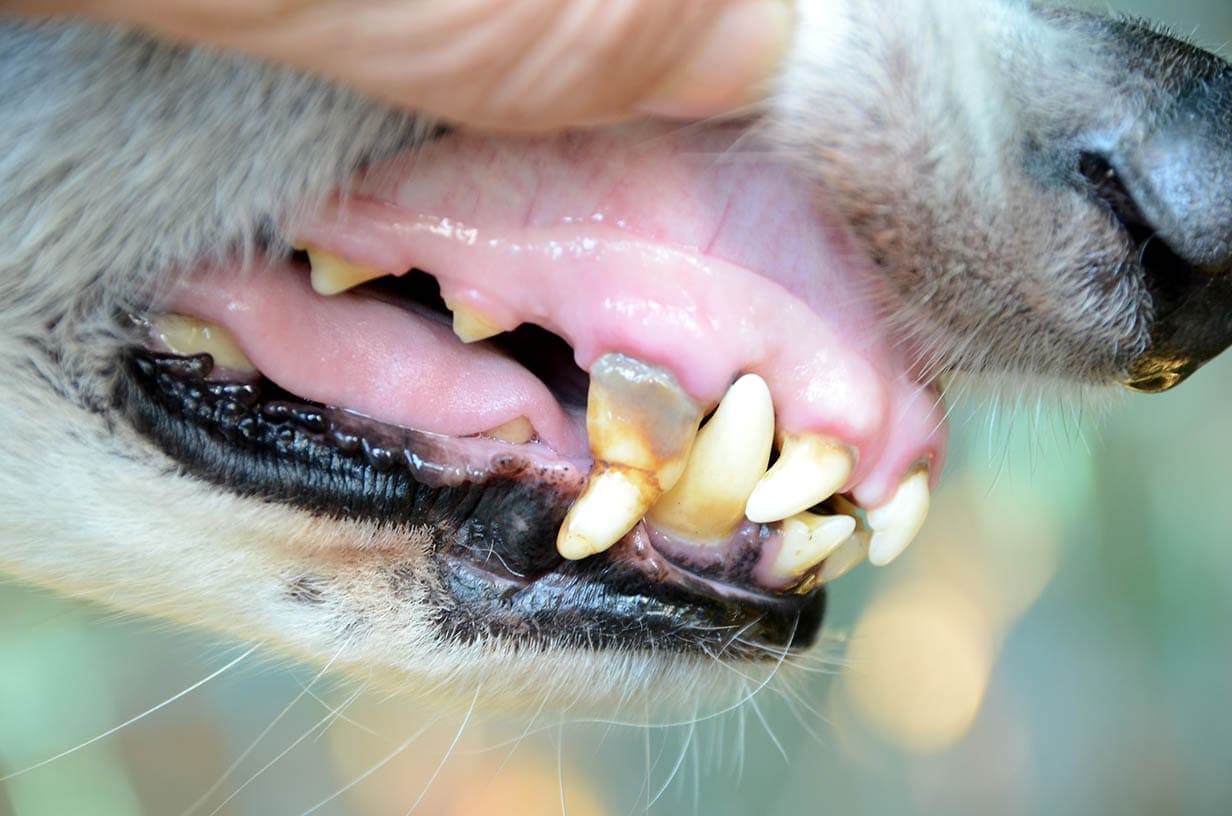
Shock can be the result of an illness or trauma and is a medical emergency that must be addressed immediately by a veterinarian. It causes a sudden decrease in blood flow throughout the body and leads to damage to organs and tissues, which in turn, can lead to the death of your pet.
- Fast breathing
- Noisy breathing
- Increased heart rate
- Weak pulse
- Pale-white mucous membranes
- Depression
- Cold extremities
- Vomiting
If your dog shows these clinical signs, take them to the vet immediately.
7. Rat Poisoning
Rat poisoning is one of the most common types of poisoning. The signs can take several days to manifest after the toxic dose has been ingested. After about 3–5 days, they become more obvious.
Rat poison causes internal bleeding. Generally, the first clinical signs include apathy (lack of energy) and pale gums. As time passes, signs like trouble breathing and collapse will occur. The internal bleeding will not be obvious (externally).
If you have seen your dog consume rat poison or suspect that this incident has occurred, contact your veterinarian immediately. Rat poisoning is fatal if not intervened in time.
How to Treat Your Dog If They Have Pale Gums
If your dog has pale gums, be sure to check for other clinical signs. If their behavior is unchanged, contact the veterinarian for advice. If your dog does show other signs, take them to the vet or the ER as soon as possible. Do not wait to see if your dog recovers on their own because you risk causing more harm.
Dog Gums Color Chart
Here is a general guide that goes over what an abnormal color of your dog’s gums can mean. That said, while this can be helpful as a reference, you should contact your veterinarian as soon as possible if your dog’s gums are a color other than pink.
| The Color of Your Dog’s Gums | Possible Causes |
| Pale pink or white | Anemia
Heart problems Internal bleeding Kidney disease Shock Blood-clotting disorder Poisoning (rat poison, heavy metals) Cancer Bloating Hypothermia |
| Yellow | Anemia
Liver problems Hemolysis |
| Slightly red | Gum irritation
Gingivitis Stomatitis |
| Bright, burgundy red | Exposure to toxins
Stroke High blood pressure Carbon monoxide poisoning |
| Blue or purple | Asthma
Lack of oxygen Suffocation Breathing difficulties Pneumonia Heart diseases Low blood pressure Hypothermia |
Conclusion
Pale gums in dogs often indicate that something is wrong with your pet. These can be caused by several conditions, such as kidney disease, heart disease, poisoning, anemia, internal bleeding, coagulation problems, etc. Healthy dogs have pink gums, and any other color can indicate a health problem. Therefore, it is recommended to contact the vet as soon as possible if you notice that your dog’s gums are pale or of a color other than pink. The clinical signs will be specific to each individual condition, so you have to keep an eye on your dog to see if you notice any other clinical signs.
See also:
Featured Image Credit: Diego Cervo, Shutterstock















