How Long Do Lionhead Rabbits Live as Pets? Vet Reviewed Lifespan, Data & Care
By Ed Malaker
Updated on

Click to Skip Ahead
The Lionhead Rabbit is a relatively new breed that is gaining popularity due to their attractive appearance. However, many people want to know how long they will live before purchasing one. The short answer is an average Lionhead rabbit lives for 7-9 years. Keep reading as we list the many factors that can affect this animal’s lifespan, like nutrition, environment, and stress.
What’s the Average Lifespan of a Lionhead Rabbit?
On average, Lionhead Rabbits live 7–9 years as pets if they are well cared for. However, some Lionhead Rabbits can live into their early teens.
Why Do Some Lionhead Rabbits Live Longer Than Others?
1. Nutrition
Proper nutrition is essential for the health and longevity of your Lionhead Rabbit. Like most rabbits, they need a diet high in fiber and low in fat. Feed them plenty of fresh hay, vegetables, and a small number of pellets to keep them from becoming overweight. Obesity can lead to several health problems and shorten their lifespan and quality of life.

2. Environment & Conditions
The living environment of your Lionhead Rabbit can affect their lifespan. These rabbits prefer to live in a clean and safe environment with plenty of room to move around, and those that do are less likely to develop health problems that can shorten their lifespan.
3. Stress
Stress can harm your rabbit’s health and lifespan. Avoid stressful situations, and provide a calm and quiet environment away from heavy foot traffic or loud conversation. Rabbits can become easily stressed by other pets (including a new rabbit) too. Pregnancy can be stressful for both female rabbits and the rabbits that share an enclosure with the pregnant female.
4. Enclosure Size/Living Quarters/Housing
A single Lionhead Rabbit will need a living space of at least 8 square feet, and we recommend adding 4 square feet for each additional rabbit that you keep in the enclosure. You will need an enclosure or hutch at least 4 feet long by 2 feet deep to create the main habitat. The enclosure should also be high enough to prevent escape. Inside the cage, you will need to place bedding, food, water, the litter box, and a hide box that they can go into when they need time alone.

5. Spaying or Neutering
Spaying or neutering your rabbit can help prevent certain health problems, such as uterine cancer in female rabbits. It can also reduce the risk of behavioral issues that can lead to stress and health problems, especially territorial problems that can occur if you have more than one female rabbit.
6. Genes
Lionhead Rabbits may inherit genes that predispose them to certain health conditions. For example, some rabbits may be more susceptible to dental problems or respiratory issues than others. Talking with your breeder about your rabbit’s ancestry can give you clues on what to expect.
7. Dental Care
Dental problems are common in rabbits and can lead to serious health issues if left untreated. Always provide your rabbit with appropriate toys to chew on, and schedule regular dental check-ups with your veterinarian to help avoid any problems.
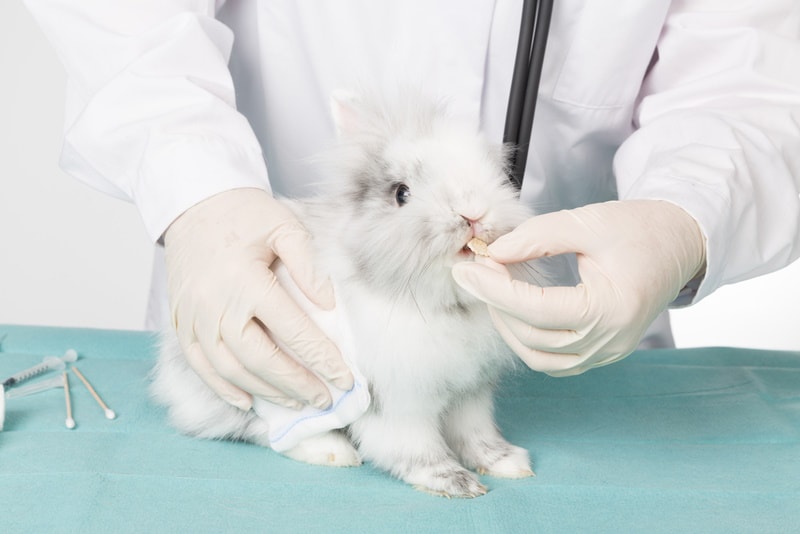
8. Healthcare
Regular veterinary check-ups can help detect and treat any health problems early on, possibly increasing your rabbit’s lifespan. Make sure to keep up with your rabbit’s vaccinations and preventative care.
The 4 Life Stages of a Lionhead Rabbit
Newborn
Lionhead Rabbits are born with closed eyes and ears and completely depend on their mother for nourishment and care. They will grow fur in 5 or 6 days, and their eyes will open in 10–12 days.

Juvenile
As the Lionhead Rabbits grow, they become more independent and curious, so they often spend a great deal of time exploring their environment. Around 3–4 months old, they reach sexual maturity and can start breeding.
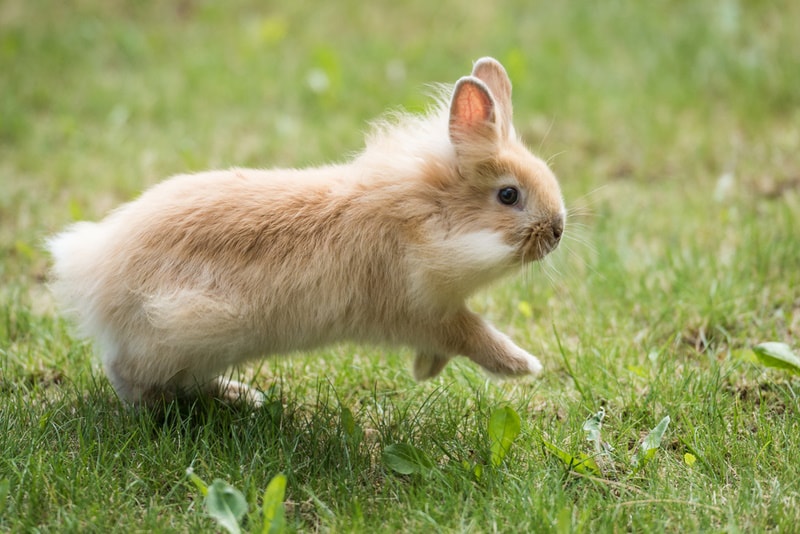

Adult
From around 6 months to 5–6 years old, the Lionhead Rabbit is considered an adult. They are fully grown and mature at this stage and unlikely to change.
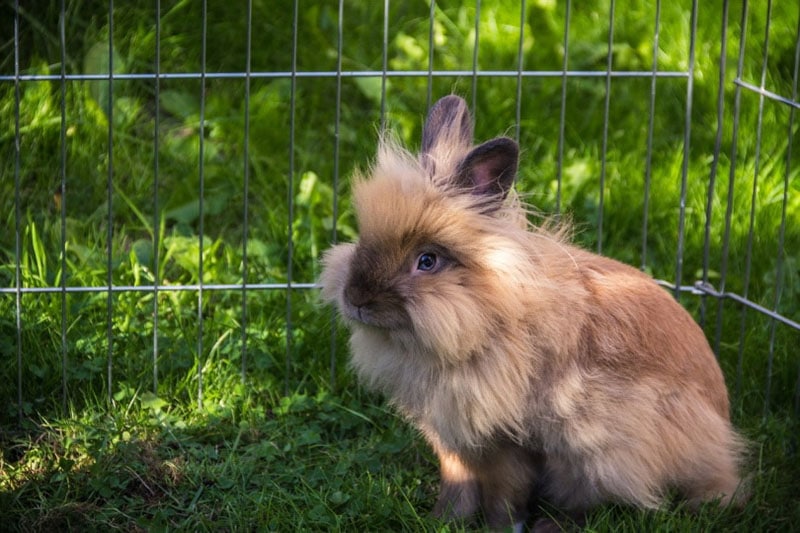

Senior
At around 5–6 years old, Lionhead Rabbits enter their senior years. Though old age in itself is not an ailment or disease, it can be a contributing factor that makes certain ailments or diseases (such as arthritis or cancer) more likely.
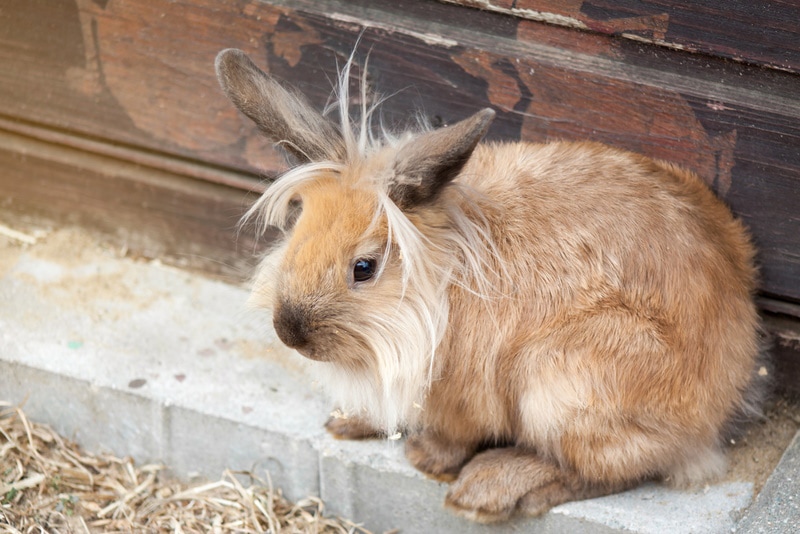

How to Tell Your Lionhead Rabbit’s Age
It can be difficult to determine the exact age of a Lionhead Rabbit. However, a few signs can give you a rough estimate. For instance, a young rabbit’s teeth will be white and sharp, while an older rabbit’s teeth may be yellow and blunt from years of wear. Generally, a rabbit’s teeth will start showing signs of wear at around 3–4 years old. You might be able to tell a senior rabbit by their comparatively duller fur, nails, feet, and lower activity levels.
Conclusion
Lionhead Rabbits are great pets that have a relatively long lifespan of 7–9 years, and you might be able to extend it even further with proper care. Providing a good habitat for your pet is essential, as is feeding them a healthy diet low in fat. Several other things can also help, like getting them spayed or neutered and making sure they see the vet regularly so you can detect any problems early.
Also Read:
- Why Do Baby Rabbits Die Suddenly? 11 Vet-Reviewed Common Reasons
- How Much Food Should a Rabbit Eat? Vet-Approved Options & Feeding Tips
Featured Image Credit: Diana Macias, Shutterstock













